Overview of Product Management 📋
Product management is the strategic process of guiding a product from conception through its lifecycle, ensuring that it meets user needs and aligns with business goals. Product managers (PMs) play a key role in defining what gets built, why it matters, and how it drives value for users and the organization.
The Product Management Process
Product management is a continuous journey that involves understanding problems, exploring potential solutions, and delivering value. The Double Diamond Framework provides a structured approach to this process, dividing it into stages of problem discovery and solution development.
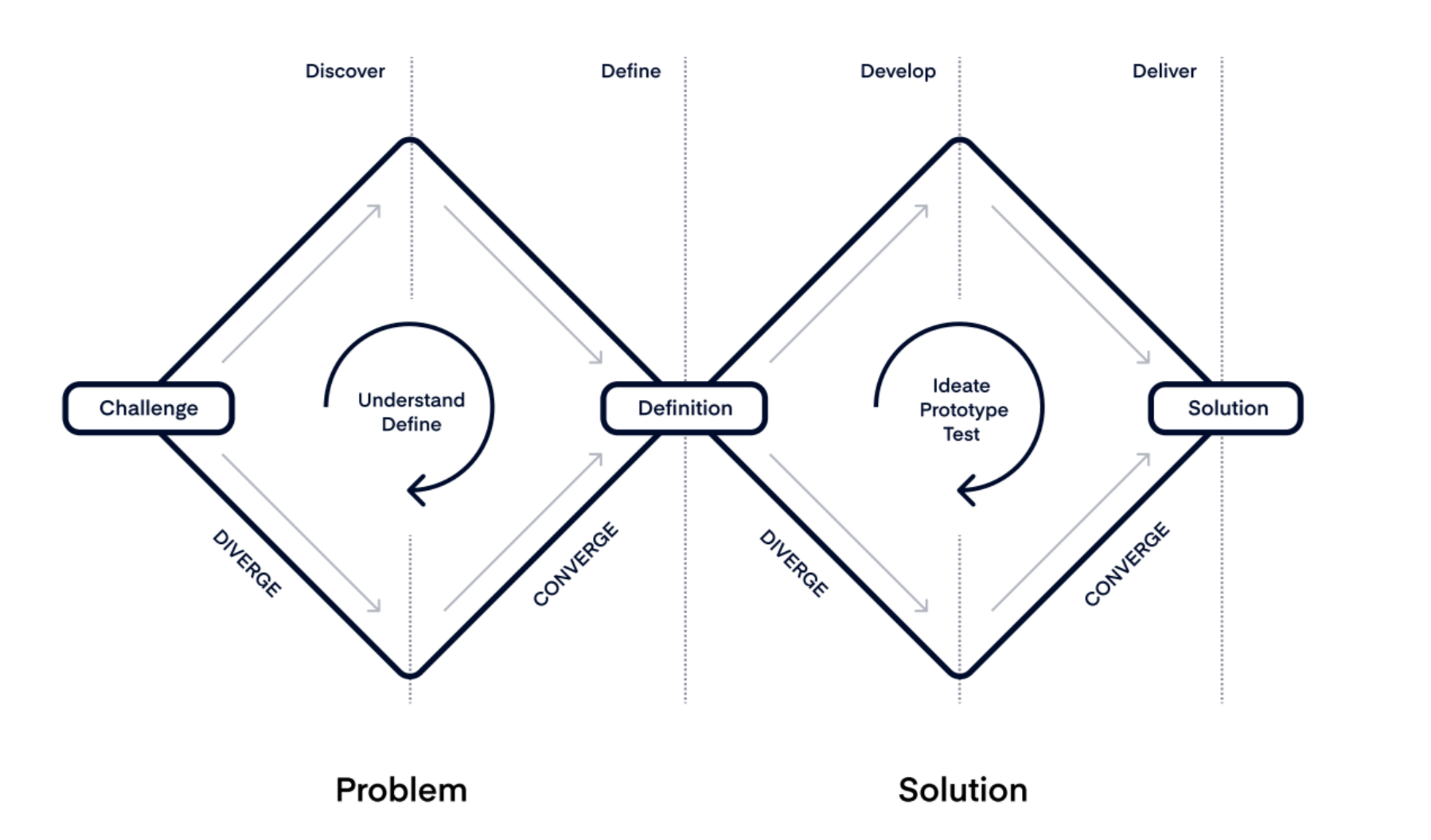
The Double Diamond Framework emphasizes exploring and refining both problems and solutions in a structured, iterative approach.
Image source: Productboard
In this framework, the product management process is divided into four key stages:
- Discover: Engage in open-ended conversations with core personas to gather unfiltered insights, avoiding preconceived notions.
- Define: Analyze collected information to identify and prioritize key problem areas, ensuring alignment with user needs and business objectives.
- Develop: Generate a range of potential solutions, encouraging creative collaboration among team members.
- Deliver: Test and refine the chosen solution, implementing it effectively to meet user needs and achieve desired outcomes.
By using this framework, product managers can approach development in a way that encourages continuous learning and improvement, with a focus on refining and validating ideas at each step.
Key Responsibilities of a Product Manager
Product managers are responsible for setting a clear product vision, defining strategy, prioritizing features, and working cross-functionally to bring products to life. Some of their core responsibilities include:
- Setting Product Vision and Strategy
- Gathering and Prioritizing Requirements
- Collaborating with Cross-Functional Teams
- Managing Roadmaps and Timelines
- Analyzing and Leveraging Data
Product management combines elements of strategy, user empathy, and leadership. By balancing user needs with business objectives, PMs create impactful products that achieve market success.